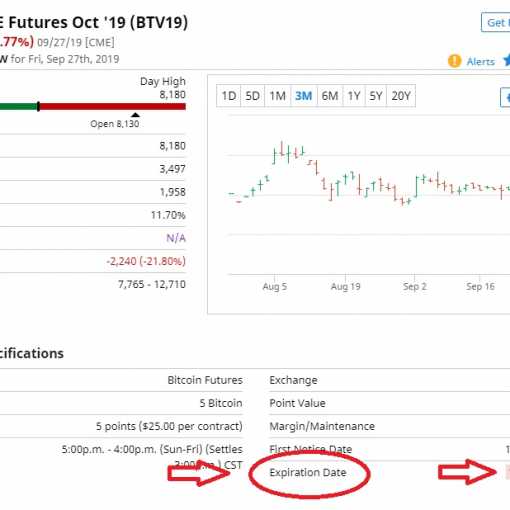
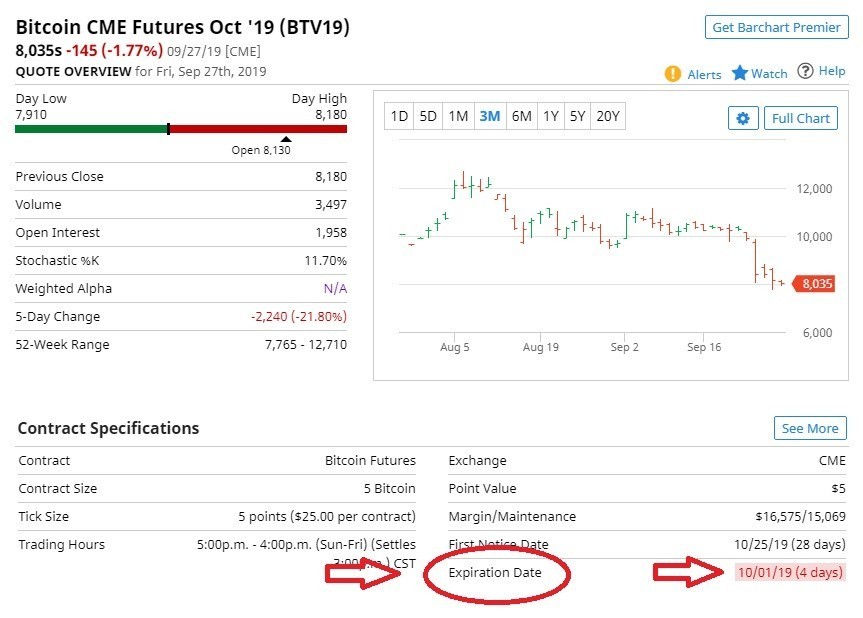
In short: Bitcoin is an electronic cash
Properties of Bitcoin:
- Bitcoin is free money, there is no one there “Manufactures”
- Bitcoin is under no institution, thus not externally Controllable
- Bitcoin is a decentralized
- Bitcoin is free and accessible (open source software)
- Bitcoin is anonymous , but with more security than other methods of payment
- Bitcoin is safe , because one of the most powerful encryption method is used
- Bitcoin is safe because it automatically checks the other side before a transfer
- Bitcoin is limited , therefore similar property like precious metals
- Bitcoin is fast , transfers will be carried out within seconds
- Bitcoin is low , because the transaction costs are minimal
- Bitcoin is low because there are no account fees
- Bitcoin is always available as server failures are completely excluded
How does the Bitcoin technology?
In 2008, the first time a white paper by Satoshi Kaka Moto has been proposed, where he described the workings of Bitcoin technology.
Each user of Bitcoin software receives a “wallet” file, this is a public and private key. The public key part serves as the address to send and receive Bitcoins, the private key part authorized these transactions. Due to random generation, the addresses do not contain any information about its owner and better exchange there is a human-readable form of 33 characters. Therefore, it is also possible the theoretically infinite number of accounts each user has, since each new generation of a key pair is like a new account. Thus, one could also use different account for different areas of everyday life.
The validation of transactions (transfers) takes place through the nodes of the network, therefore, is on each transaction of the public key part contained in Bitcoin replaced by its new owner and signed with the private key part. About the Tiger Tree Hash each transaction is recorded in the Bitcoin database, double spending thus be prevented.
New Bitcoins are generated distributed through the solution of complex mathematical problems on the computer network, while the upper limit is the maximum existing Bitcoins 21 million. However, each Bitcoin are 10 ^ 8 divided, thus this gives a maximum limit of Bitcoins in the amount of 2.1 * 10 ^ 15 units.
‘s New Bitcoins are calculated by the formula: (6 * 50 bitcoins / hour) * (own CPU speed / sum of total CPU speed of the network) . Thus, for example, generation of 50 Bitcoins would take on a standard computer about 1 year, therefore, the generation on a large scale is only worthwhile when using GPU’s or distribute computer networks.
Address
A Bitcoin address is similar to a physical address or an email. It is the only information you need to provide for someone to pay you with Bitcoin. An important difference, however, is that each address should only be used for a single transaction.
Bit
Bit is a common unit used to designate a sub-unit of a bitcoin – 1,000,000 bits is equal to 1 bitcoin (BTC or B⃦). This unit is usually more convenient for pricing tips, goods and services.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin – with capitalization, is used when describing the concept of Bitcoin, or the entire network itself. e.g. “I was learning about the Bitcoin protocol today.”
bitcoin – without capitalization, is used to describe bitcoins as a unit of account. e.g. “I sent ten bitcoins today.”; it is also often abbreviated BTC or XBT.
Block
A block is a record in the block chain that contains and confirms many waiting transactions. Roughly every 10 minutes, on average, a new block including transactions is appended to the block chain through mining.
Block Chain
The block chain is a public record of Bitcoin transactions in chronological order. The block chain is shared between all Bitcoin users. It is used to verify the permanence of Bitcoin transactions and to prevent double spending.
BTC
BTC is a common unit used to designate one bitcoin (B⃦).
Confirmation
Confirmation means that a transaction has been processed by the network and is highly unlikely to be reversed. Transactions receive a confirmation when they are included in a block and for each subsequent block. Even a single confirmation can be considered secure for low value transactions, although for larger amounts like 1000 US$, it makes sense to wait for 6 confirmations or more. Each confirmation exponentially decreases the risk of a reversed transaction.
Cryptography
Cryptography is the branch of mathematics that lets us create mathematical proofs that provide high levels of security. Online commerce and banking already uses cryptography. In the case of Bitcoin, cryptography is used to make it impossible for anybody to spend funds from another user’s wallet or to corrupt the block chain. It can also be used to encrypt a wallet, so that it cannot be used without a password.
Double Spend
If a malicious user tries to spend their bitcoins to two different recipients at the same time, this is double spending. Bitcoin mining and the block chain are there to create a consensus on the network about which of the two transactions will confirm and be considered valid.
Hash Rate
The hash rate is the measuring unit of the processing power of the Bitcoin network. The Bitcoin network must make intensive mathematical operations for security purposes. When the network reached a hash rate of 10 Th/s, it meant it could make 10 trillion calculations per second.
Mining
Bitcoin mining is the process of making computer hardware do mathematical calculations for the Bitcoin network to confirm transactions and increase security. As a reward for their services, Bitcoin miners can collect transaction fees for the transactions they confirm, along with newly created bitcoins. Mining is a specialized and competitive market where the rewards are divided up according to how much calculation is done. Not all Bitcoin users do Bitcoin mining, and it is not an easy way to make money.
P2P
Peer-to-peer refers to systems that work like an organized collective by allowing each individual to interact directly with the others. In the case of Bitcoin, the network is built in such a way that each user is broadcasting the transactions of other users. And, crucially, no bank is required as a third party.
Private Key
A private key is a secret piece of data that proves your right to spend bitcoins from a specific wallet through a cryptographic signature. Your private key(s) are stored in your computer if you use a software wallet; they are stored on some remote servers if you use a web wallet. Private keys must never be revealed as they allow you to spend bitcoins for their respective Bitcoin wallet.
Signature
A cryptographic signature is a mathematical mechanism that allows someone to prove ownership. In the case of Bitcoin, a Bitcoin wallet and its private key(s) are linked by some mathematical magic. When your Bitcoin software signs a transaction with the appropriate private key, the whole network can see that the signature matches the bitcoins being spent. However, there is no way for the world to guess your private key to steal your hard-earned bitcoins.
Wallet
A Bitcoin wallet is loosely the equivalent of a physical wallet on the Bitcoin network. The wallet actually contains your private key(s) which allow you to spend the bitcoins allocated to it in the block chain. Each Bitcoin wallet can show you the total balance of all bitcoins it controls and lets you pay a specific amount to a specific person, just like a real wallet. This is different to credit cards where you are charged by the merchant.